Dealing with Dates and Time Zones
Microsoft announced the Retirement of Exchange Web Services in Exchange Online a while ago. That means vendors and any scripts or applications you have written should be reviewed and rewritten to use Microsoft Graph.
One of the little things that can bite you are dates and times.
The Issue with Dates
I was involved in a project where an existing application was rewritten to utilize Microsoft Graph instead of Exchange Web Services. One of the features was related to tasks. Microsoft Graph supports tasks with the To Do API.
The problem the project team faced was that the time format used was never converted to the users’ respective time zones. As a result, all the date and time stamps, for example, dueDateTime, were wrong.
Why Does This Happen?
When using Exchange Web Services, the API establishes a connection to the mailbox. This allows several pieces of information, like time zone settings, to be known. The EWS API converts the given date-time values from UTC into the respective time zone of the mailbox and uses the converted value for creation.
Microsoft Graph does not include this functionality, which means that developers must pay more attention to date and time values in their programs and scripts during the transition from EWS to the Graph APIs.
How the Graph Handles DateTime Values
Microsoft Graph uses the ISO 8601 format for dateTime values, and if no time zone information is given in the request, UTC is assumed.
When you look at the properties dateTimeTimeZone resource type provides, you see two properties. While dateTime is required, timeZone is an optional property.
Finding Date and Time Zone Settings
There are multiple ways to ensure that correct time stamps are in place. One is to use the timeZone set on the mailbox.
Because Microsoft Graph is stateless, you must query the mailbox to fetch the property. You can retrieve the mailbox’s timeZone via the /mailboxSettings endpoint:
Figure 1 shows how to connect to Microsoft Graph with the required scopes and store the settings in a variable:
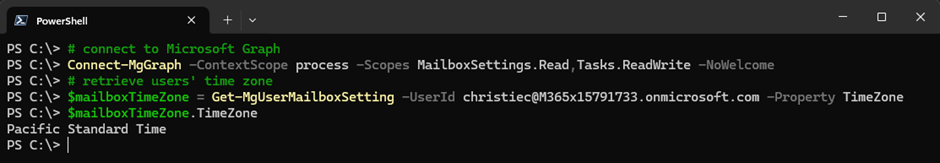
Code used:
# connect to Microsoft Graph Connect-MgGraph -ContextScope process -Scopes MailboxSettings.Read,Tasks.ReadWrite -NoWelcome # retrieve users' time zone $mailboxTimeZone = Get-MgUserMailboxSetting -UserId <user’s UPN> -Property TimeZone
Now that we know the users’ time zone, we can use this information to create a request with the following code:
# create the details of the task
$details = @{
title = 'Practical 365'
dueDateTime = @{
dateTime = '2024-11-15T17:00:00';
timeZone = $mailboxTimeZone.TimeZone
}
importance = 'high'
}
# build parameters for cmdlet
$paramsNewTask = @{
UserId = 'christiec@M365x15791733.onmicrosoft.com'
BodyParameter = $details
TodoTaskListId = 'Tasks'
}
# create the task
$task = New-MgUserTodoListTask @paramsNewTask
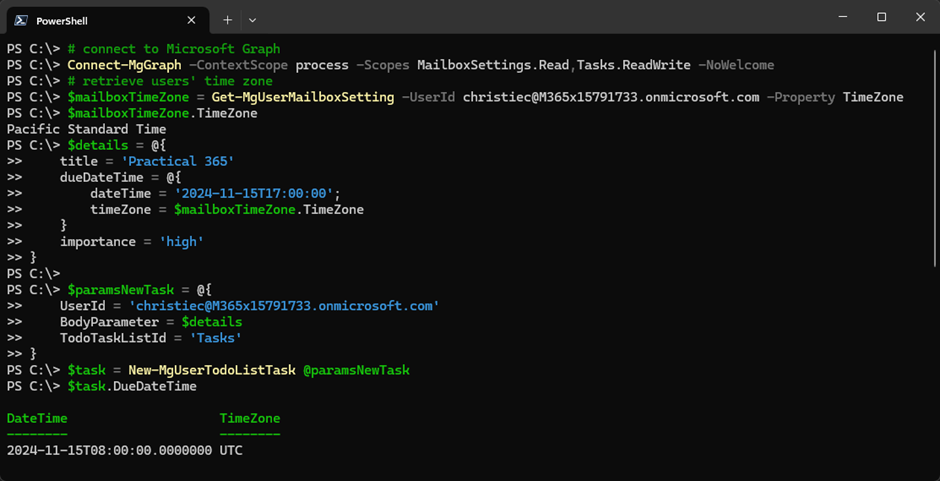
Figure 2 shows the task created. You can see that the dueDateTime property is adjusted. I created this task from a machine with a UTC+1 time zone, while the target time zone is UTC-8: 9 hours difference!
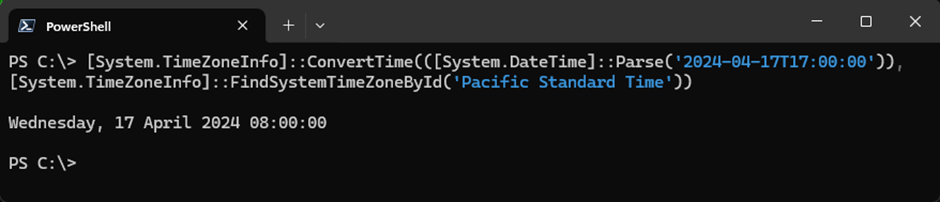
Another way is to convert the value using the .NET System.TimeZoneInfo. The following code will convert the given time stamp ‘2024-04-17T17:00:00‘ into the mailbox’s configured time zone ‘Pacific Standard Time‘:
[System.TimeZoneInfo]::ConvertTime(([System.DateTime]::Parse('2024-04-17T17:00:00')), [System.TimeZoneInfo]::FindSystemTimeZoneById('Pacific Standard Time'))
Figure 3 shows the same result as in our previous example:
Be Careful!
With both methods, you should ensure that the timestamp is in the proper format and that the timeZone property is used. The following examples show why:
ISO 8601 allows you to define UtcOffSet (either Z or +hh:mm or -hh:mm). When you do this, conversion takes place 2 times. Figure 4 shows this:
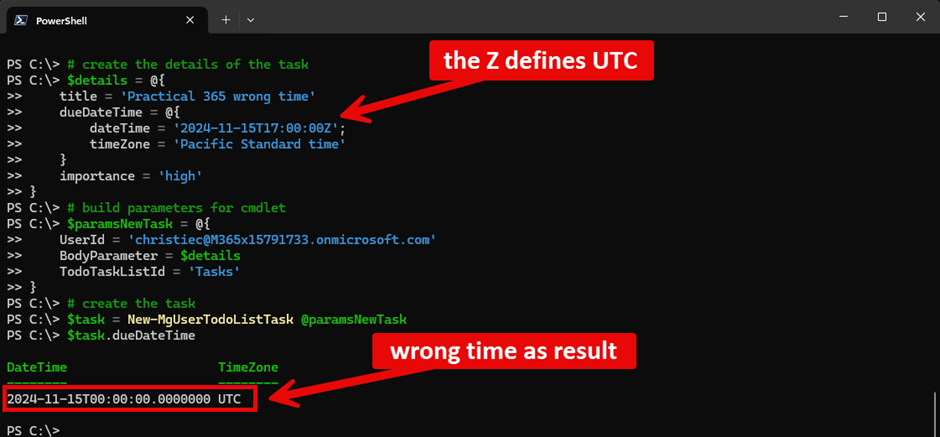
This is crucial to know. Also, .NET uses the machine’s time zone settings for any conversion. Ensure you have the correct settings in place and proper testing before using it in production!
Conclusion
Dealing with date and time values can be very tricky and confusing. Inside Microsoft 365, dates and times are important to many applications, so this topic is very important to keep an eye on.
At this point, I want to emphasize that before EWS is retired, Microsoft will retire EWS ApplicationImpersonation very soon: February 2025! My Practical 365 article explains how to migrate to Exchange Online RBAC.





Hello, I hope you and your family are doing well! I’ve been reading your articles—they’re excellent!
I’m currently testing message migration between Exchange Online tenants using the Graph API. One of the main issues I’m facing is that the messages are being migrated to the Drafts folder in the target mailbox, and their original dates are not preserved—they’re replaced with the migration execution date.
Have you encountered this before? Do you have any suggestions or workarounds?
Thank you in advance!
Hi Carlos,
Thank you!
Regarding your problem: I firmly believe this is by design. You don’t migrate the message. You read from the source and create in the target. I don’t think there is a fix or workaround for this. The only way for migration might be the import/export API, which is in preview:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/graph/mailbox-import-export-concept-overview?WT.mc_id=M365-MVP-5001727
Ciao,
Ingo
Hi Tomas,
Unfortunately, this option is one of the many missing features in Microsoft Graph. I can tell you that we (MVPs, partners, and large customers) give the PG strong feedback about this list!
Hello Ingo, thank you for the article.
With the upcoming end of EWS access I’m facing one specific challenge and I’m wondering if you might have any tips. I’m using EWS to store existing EML files into a mailbox (archiving) simply by setting MimeContent of Data.EmailMessage and calling Save. As far as I know, this is not possible with Graph API (it can only created new email messages, not import existing ones with all headers). Do you know about a feature in Graph API or any other way, that would allow this?
Thank you for your help.