Standard vs. Premium Journaling
Journaling is a Functionality that has roots back to Exchange 5.5 SP1, where it could be implemented as MTA Journaling. In current versions of Exchange, you can set up Journaling so that the server sends copies of all messages it processes to a Journal recipient. Two types of Journaling can be implemented:
Standard Journaling – Configured on mailbox databases, standard journaling copies all messages sent to or from the mailboxes on that database. Standard Journaling is configured in the properties of the mailbox database or by running the Set-MailboxDatabase cmdlet.
Premium Journaling – Configured using journal rules, premium journaling can copy all messages sent within an organization. Journal rules can be applied in a more targeted manner than standard journaling. You can configure journal rules to only journal external email or to only journal email for specific recipients in the organization. Journal rules are configured in the compliance management section of the Exchange admin center or by running the New-JournalRule cmdlet:
Set-MailboxDatabase MDB01 -JournalRecipient journaling@icewolf.ch Get-MailboxDatabase MDB01 | fl Name, JournalRecipient
For more information, see this article: Exchange Best Practices: Configuration of Database Hosting Journal Mailbox
Exchange Online Journaling
While Microsoft recommends using Microsoft 365 Retention to retain data in Exchange Online when possible, there might still be some good reasons to use Journaling:
- If you’re in a Hybrid environment, you will want to have all email data in one place.
- The maturity of the organization. In other words, you need more time to implement a Data Lifecycle with retention.
- The 3rd party archiving or compliance product lifecycle or lifespan has not yet expired.
- The use of 3rd party SaaS products for compliance or security.
In Exchange Online, you don’t have access to mailbox databases. But you still can use Journaling Rules to send copies of messages to a Journal Recipient. The big prerequisite is that the recipient must be outside of Exchange Online. You can’t designate an Exchange Online mailbox as a journaling mailbox. You can deliver journal reports to an on-premises archiving system or a third-party archiving service.
To set up Journaling in Exchange Online, administrators must configure Journaling rules. These rules define which emails are Journaled and where the copies are sent. There are two types of Journaling rules in Exchange Online: standard rules and scoped rules.
Standard Journaling rules apply to all messages that match a set of criteria defined by the administrator, such as messages sent to or from a particular user or distribution group. When a message matches a standard Journaling rule, a copy of that message is sent to the designated mailbox or archive.
Scoped Journaling rules are similar to standard rules, but they apply only to a specific set of users, such as a particular department or business unit. This allows organizations to limit the scope of Journaling to only those users or groups that require it, reducing the amount of data that needs to be stored and reviewed.
Journaling Rules are configured in the Data lifecycle management section of the Microsoft Purview compliance portal under Exchange (legacy).
Journaling Rules consist of three aspects, as seen in Figure 1 below.
- Journal Recipient (the email address where the Journal Messages are sent to)
- Journaling Mailbox (everyone or a specific Mailbox, Contact, or Distribution Group)
- Journal Scope (all messages / Internal messages only / External messages only)
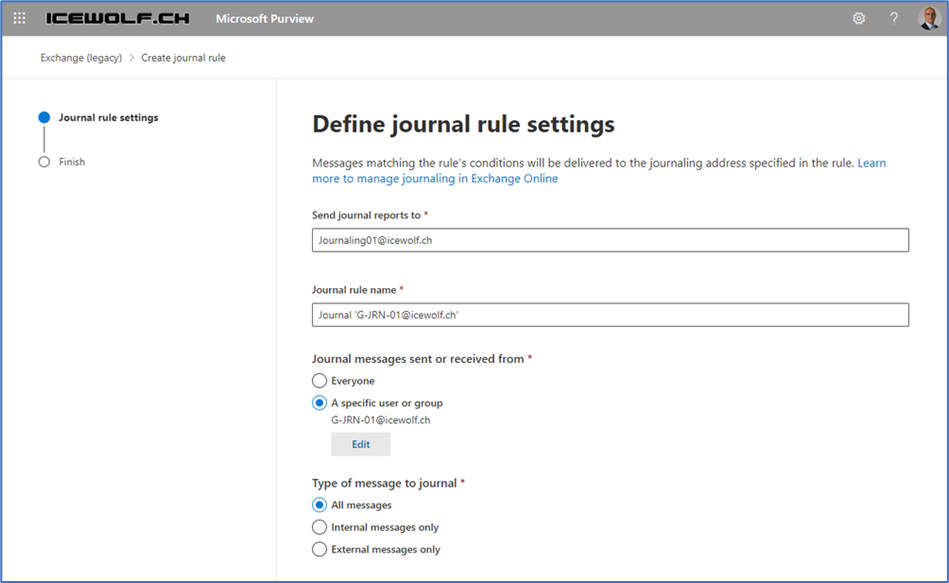
Here’s the PowerShell command to create a Journaling Rule based on the membership of a Distribution Group for all messages.
New-JournalRule -Name "Journal in ‘G-JRN-01@icewolf.ch’" -Recipient G-JRN-01@icewolf.ch -JournalEmailAddress "Journaling01@icewolf.ch" -Scope Global -Enabled $True
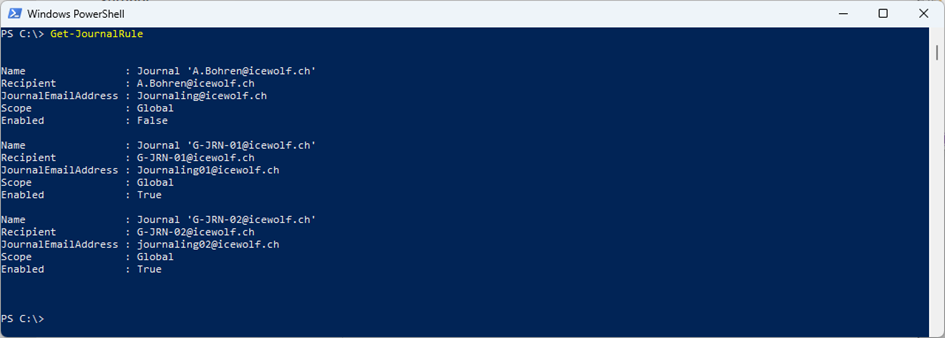
To view the Journaling Rules in Exchange Online, use the following command as seen in Figure 2 below:
Get-JournalRule
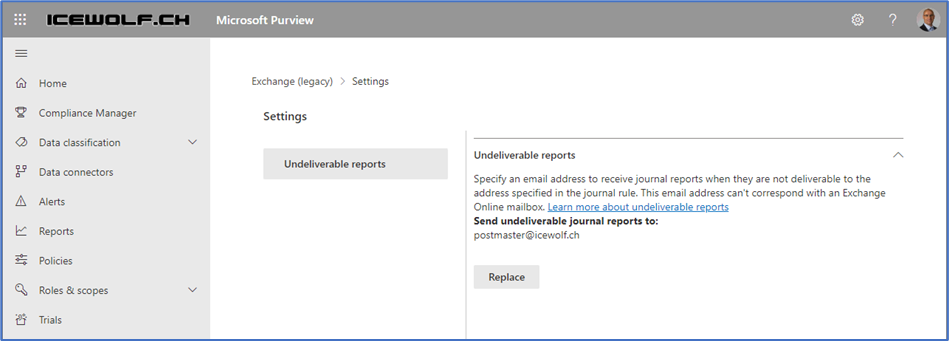
Under Additional Settings, you need to configure the NDR Recipient if Exchange Online can’t deliver messages to the Journaling Recipient, as seen in Figure 3.
To get informed when there is a problem with reaching the Journaling Recipient, it’s recommended that you set the JournalingReportNdrTo parameter in the transport configuration to point to an external address, as seen in Figure 4 below.
Set-TransportConfig -JournalingReportNdrTo postmaster@icewolf.ch Get-TransportConfig | fl *journ*
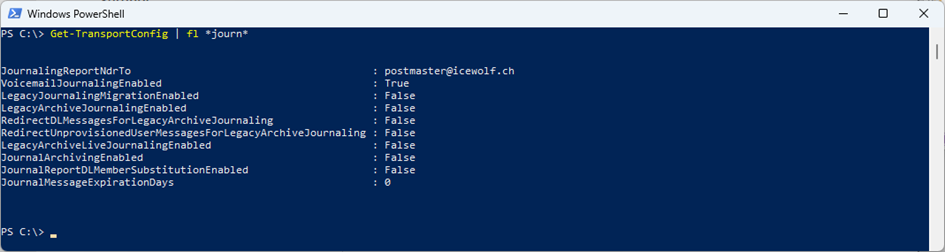
Depending on the Policies of your Organization you might not need to Journal VoiceMail. In that case you can change the Parameter VoiceMailJournalingEnabled to $false. If you want to increase the time before the Journal Messages in the queue expire, you can use the JournalMessageExpirationDays Parameter, as explained in the table below.
| Parameter | Explanation |
| JournalingReportNdrTo | External Emailaddress (empty by default), for example, an on-premises Shared Mailbox. |
| VoiceMailJournalingEnabled | The VoicemailJournalingEnabled parameter specifies whether Unified Messaging voice mail messages are journaled by the Journaling agent. The default value is $true. |
| JournalMessageExpirationDays | Integer from 0 to 7. The default value is 0, which means undeliverable journal reports are treated like regular undeliverable messages. |
In recent migrations from Exchange Server to Exchange Online, my plan was always to add the mailboxes to different Journaling Groups. That way, we could distribute the load to multiple Journaling recipients. Depending on the requirements, there can be multiple ways to achieve this:
- Based on UPN Suffix or Domain of PrimarySMTPAddress
- Based on Company / Department or Business Unit
- Based on First Character of Lastname or First Character of Emailaddress
Journaling in a Hybrid Scenario
If your organization is set up in a hybrid deployment, you must configure any Journaling rules twice, once in the on-premises Exchange Server and an identical rule in Exchange Online. If you don’t, some messages might not be journaled.
If the sender and recipients are both in accepted domains of the same organization, the messages are not honored as external, even if the x-ms-exchange-crosstenant-authas header in the messages has the value anonymous. Accordingly, these messages are not Journaled as external.
A few days ago, the Exchange Team released additional Information for Journaling in Hybrid Scenarios.
Scenario 1: MX Record Points to On-Premises
When email is processed by on-premises first, a header called X-MS-Exchange-Organization-Processed-By-Journaling is added by Exchange Server to indicate that the Journaling agent touched the message. Regardless of whether any on-premises Journaling rule exists, the Journaling agent will always touch a message on-premises, and the header will be added. It is not possible to disable the on-premises Journaling agent.
When an email is sent from on-premises to Exchange Online, it will be sent to the remote routing address (tenant.mail.onmicrosoft.com) and then in Exchange Online, the categorizer resolves the address to the primary address which is contoso.com. Because of this change, Journaling happens again in Exchange Online.
When Send from Alias is enabled, the Exchange Online address resolution from tenant.mail.onmicrosoft.com to consoso.com does not happen (to preserve the alias) and there will be no change in the email address. So, with the Send From Alias feature enabled, Journaling by Exchange Online does not happen when an email originated from or was routed through on-premises.
A few months ago, I had such a case and figured it out by Exchange pipeline tracing. Using Pipeline tracing captures copies of email messages from a specific SenderAddress as they move through the transport pipeline in the Transport service or the Mailbox Transport service on Mailbox server and on Edge Transport servers.
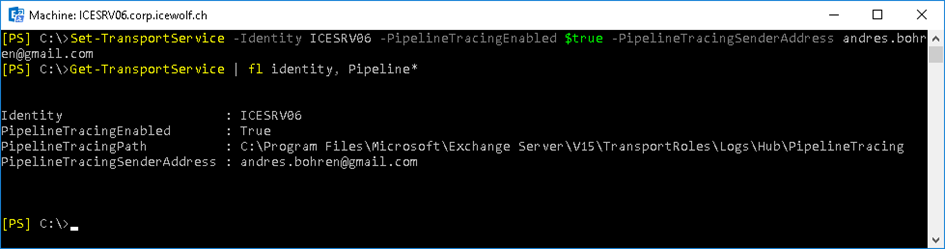
To enable Pipeline Tracing use the following Command as in Figure 5 below.
Set-TransportService -Identity <ServerName> -PipelineTracingEnabled $true -PipelineTracingSenderAddress <senderaddress>
To review your settings use the following command:
Get-TransportService | fl Identity, Pipeline*
In Figure 6, you can see the Header X-MS-Exchange-Organization-Processed-By-Journaling.
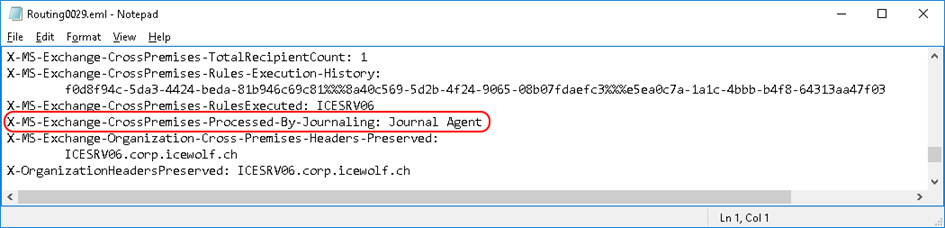
That header is not visible in the destination Mailbox in Exchange Online. To fix this issue you need to create a Transport Rule on the on-premises Exchange Server to remove the header.
New-TransportRule "Remove JournalingHeader" -RecipientAddressContainsWords "icewolfch.mail.onmicrosoft.com" -RemoveHeader "X-MS-Exchange-Organization-Processed-By-Journaling" -enabled $true
Scenario 2: MX Record Points to Exchange Online
When an MX record points to Exchange Online, the Exchange Online Journaling agent processes the email first. In this case, centralized mail routing plays an important role in how Journaling works on inbound emails.
When centralized mail routing is enabled:
- Inbound emails are routed to On-premises first, regardless of whether the recipient is located. However, before that, the Exchange Online Journaling agent will add the header X-MS-Exchange-Organization-Processed-By-Journaling. The header will be promoted on the email to on-premises. Regardless of any Journaling rule in Exchange Online, the agent will always touch a message, and the header will be added. Like Exchange Server, it is not possible to disable this agent in Exchange Online.
- Exchange Server will initially skip journaling for on-premises recipients because of the presence of the header.
- However, for Exchange Online recipients, the Exchange Server categorizer resolves the address contoso.com to the target address, which is Contoso.mail.onmicrosoft.com. Because of this change, Journaling does happen in Exchange Server for Exchange Online recipients if there is a matching journaling rule on-premises.
- Similarly, when email gets routed back to Office 365, Journaling happens again in Exchange Online for the second time as the categorizer resolves the contoso.mail.onmicrosoft.com to the primary domain contoso.com for Exchange Online recipients.
Wrapping Up
It’s crucial to understand how Exchange Journaling works and that Settings like SendFromAlias, Centralized Mail Routing, and where your MX record points to, have a huge impact on Journaling. Make sure you test everything thoroughly before you implement Journaling at scale. After the implementation make sure you have set JournalingReportNdrTo in TransportConfig, so you notice when Emails can’t be delivered to the Journaling Recipient. Otherwise, you might end up with a compliance gap.




Hi Andres
I have Send As Alias enabled, so an email from an on-premise mailbox to an EOL mailbox does not get journaled by the journaling rule in Exchange online.
Thanks to your article, through pipeline tracing I could see the “X-MS-Exchange-Organization-Processed-By-Journaling: Journal Agent” header was added to the email.
I created a Transport Rule to remove the header, but it’s still not journaling, and does not appear to be removing the “X-MS-Exchange-Organization-Processed-By-Journaling: Journal Agent” header.
From the look of it, the “X-MS-Exchange-Organization-Processed-By-Journaling: Journal Agent” header gets added in the Routing0022.eml file.
X-MessageSnapshot-UTC-Time: 2024-07-17T13:42:16.802Z
X-MessageSnapshot-Source: OnRoutedMessage,Journal Agent
While the Transport Rules get processed in the Routing0013.eml file, and occurs about a second before the header gets added.
X-MessageSnapshot-UTC-Time: 2024-07-17T13:42:15.826Z
X-MessageSnapshot-Source: OnResolvedMessage,Transport Rule Agent
I tested removing a header that exists in the Original.eml file, so before the Transport Rules get processed, and that gets removed.
I also found that the Journal Agent is mentioned in the Routing0009.eml file, so before the Transport Rules, but doesn’t add the header.
X-MessageSnapshot-UTC-Time: 2024-07-17T13:42:15.806Z
X-MessageSnapshot-Source: OnSubmittedMessage,Journal Agent
For some context, I have Standard Journaling enabled on all databases, but have also setup Premium Journaling on my test mailboxes to see if that results in the “X-MS-Exchange-Organization-Processed-By-Journaling: Journal Agent” header been added in the Routing0009.eml file, so before the Transport Rules are processes, but it doesn’t seem to.
Are you able to offer any advice on how I can remove the “X-MS-Exchange-Organization-Processed-By-Journaling: Journal Agent” header, so that I can journal the email in EOL?
Thanks
Mike
Hi Mike,
As stated here:
https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/exchange-team-blog/journaling-in-hybrid-scenarios/ba-p/3821516
What happens when Send From Aliases is enabled?
When this feature is enabled, the Exchange Online address resolution from contoso.mail.onmicrosoft.com to consoso.com does not happen (to preserve the alias) and there will be no change in the email address. So, with Send From Alias feature enabled, journaling by Exchange Online does not happen when email originated from or was routed through on-premises.
That’s seems to be true according to my Tests.
Kind Regards
Andres
Hi Miles,
As documented by Microsoft here: https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/exchange-team-blog/journaling-in-hybrid-scenarios/ba-p/3821516
Scenario 1: MX record points to on-premises
When email is processed by on-premises first, a header called X-MS-Exchange-Organization-Processed-By-Journaling is added to indicate that the journaling agent touched the message (this is an internal header and won’t be visible to the recipient). Regardless of whether any on-premises journaling rule exists, the journaling agent will always touch a message on-premises, and the header will be added. It is not possible to disable the on-premises journaling agent. This header will be promoted on the email to Exchange Online, and once in Exchange Online, the service won’t journal the email again to prevent duplicate journaling.
Kind Regards
Andres
“That header is not visible in the destination Mailbox in Exchange Online. To fix this issue you need to create a Transport Rule on the on-premises Exchange Server to remove the header.”
If that journal header is not visible in EXO, why create a rule to remove it?
I would think that the header is maintained, since Exchange on-premises and Exchange Online treat hybrid messages as internal because the email addresses have the same accepted domain. Does removing that header force the other Exchange environment to journal it again?